The Biochemistry Behind Collagen Synthesis In The Human Body
It’s not as simple as just consuming a collagen supplement. The synthesis process on its own is already of high complexity!
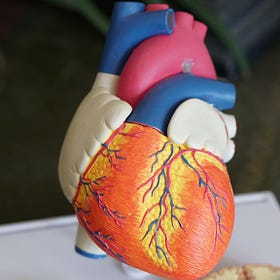
We do know of collagen as this structural protein in our body. It’s a protein that supports the physical structure of our skin and our joints. We can even find it in our bones. It even seals off the atherosclerotic plaques that are prevalent in heart disease patients.
Collagen is a protein like any other protein in the body. There are many different types of amino acids in the body, and a combination of them will result in the synthesis of a protein molecule. Specific combinations yield specific types of proteins, and collagen is no exception to that.
What Pain In The Joints Indicates For The Rest Of Our Body.
Osteoarthritis is a common issue that plagues most people who experience chronically painful joints that have lost a fraction of their original functions. We feel it as we age and as our bodies degenerate.
How Osteoporosis Isn’t Just About A Calcium Deficiency
The adult human body’s skeleton comprises 206 bones. They support our frame and our structure. We need them to stand up and walk. We need them to move about.
Now, Seriously, What's So Tricky About Cholesterol?
This article is the final part of a 3 part miniseries. The first 2 parts can be found at:
There are multiple types of collagen present in our body, each having their own part to play in how the body functions.
But what we have are 3 dominant amino acids in the structure of collagen — glycine, proline and lysine. The genetic coding for collagen synthesis is encoded into the DNA of fibroblast cells for these cells to produce collagen accordingly — and of course, as we age, the production efficiency and the quantity of collagen being produced decreases. As we age, too, the rate of coly.lagen destruction actually increases too, so we’re actually facing a double whamm
While glycine and proline aren’t that necessarily reactive, lysine contains an additional amino (-NH2) group that the lysyl oxidase enzyme targets and converts into an aldehyde. Two aldehyde groups on neighbouring collagen protein strands can react with each other in an aldol condensation reaction, which then results in the cross-linking of these collagen protein strands.
Even though these 3 amino acids are the major constitutents, the collagen protein does contain all the other naturally occurring amino acids in its structure, and Vitamin C is necessary for facilitating the synthesis of collagen itself.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to The Biochemistry Of Human Health to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.